

Next: The forward curve
Up: Properties of the term
Previous: Unconditional finite-time yield dynamics
Define 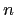 zero-rates
zero-rates
 as key rates, then
as key rates, then
 ,
i.e. arbitrary rates
,
i.e. arbitrary rates
 can be reexpressed in terms of the key-rates
can be reexpressed in terms of the key-rates
 |
(18) |
and the conditional yield change
 is
is
i.e.
![$E\left[{\Delta\mathsf y}\vert{\mathsf y_{\mathrm{kr}}}_0\right]$](img81.png) is affine in
is affine in
 :
:
![\begin{displaymath}
E\left[{\Delta\mathsf y}\vert{\mathsf y_{\mathrm{kr}}}_0\ri...
...athsf U_{\mathrm{kr}}^-{\mathsf v}-\mu_\infty)\right] \quad .
\end{displaymath}](img83.png) |
(19) |
Markus Mayer
2009-06-22
