

Next: Expected excess returns and
Up: The general -factor Gaussian
Previous: Conditional finite-time yield dynamics
The forward rate 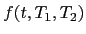 at time
at time 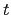 is defined as
is defined as
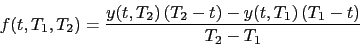 |
(20) |
and the instantaneous forward rate 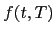 at time t is
at time t is
![\begin{displaymath}
f(t,T) = \lim_{T_1\to T_2} f(t,T_1,T_2) = \frac{\partial\left[(T-t)\,y(t,T)\right]}{\partial T} \quad .
\end{displaymath}](img88.png) |
(21) |
Inserting the expression for 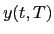 yields
yields
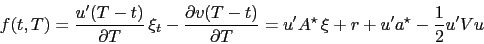 |
(22) |
where it is understood that 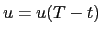 ,
, 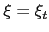 , etc.
, etc.
Short end slope The short end of the instantaneous forward curve is naturally related the short end of the
zero curve, but also contains information about risk premia: Since
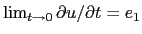 the short-end forward slope is
the short-end forward slope is
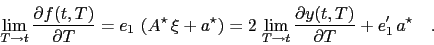 |
(23) |
Markus Mayer
2009-06-22
![]() the short-end forward slope is
the short-end forward slope is