

Next: Unconditional finite-time yield dynamics
Up: Properties of the term
Previous: Slope of the short
The covariance structure of zero-rates 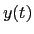 can be obtained right away.
With
can be obtained right away.
With
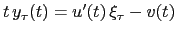 the conditional zero-rates follow the process
the conditional zero-rates follow the process
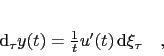 |
(14) |
where
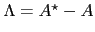 ,
,
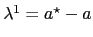 ,
and the instantaneous conditional covariances are
,
and the instantaneous conditional covariances are
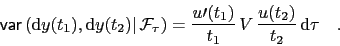 |
(15) |
The results of section ![[*]](crossref.png) on eigenvalues of outer
product matrices shows thet the covariances
on eigenvalues of outer
product matrices shows thet the covariances
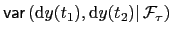 have exactly
have exactly 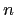 positive
eigenvalues (counting multiplicities).
positive
eigenvalues (counting multiplicities).
Markus Mayer
2009-06-22
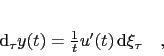
![[*]](crossref.png) on eigenvalues of outer
product matrices shows thet the covariances
on eigenvalues of outer
product matrices shows thet the covariances