

Next: Short observation times
Up: OU-processes
Previous: Maximum likelihood estimation
Define
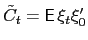 which satisfies the ODE
which satisfies the ODE
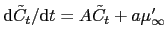 , i.e.
, i.e.
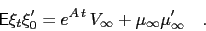 |
(76) |
The auto(cross-)covariance and auto(cross-)correlation functions are therefore
The Fourier transform of the autocorrelation function is the power spectrum:
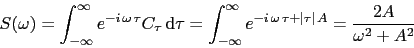 |
(79) |
(use
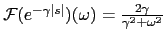 .)
If the eigenvalues of
.)
If the eigenvalues of 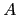 are
are
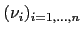 the eigenvalues of
the eigenvalues of 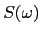 are
are
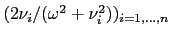 . If the observed process is an affine
function of the state process
. If the observed process is an affine
function of the state process 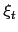 , i.e.
, i.e.
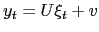 , the observed autocovariance
and autocorrelation function are
, the observed autocovariance
and autocorrelation function are
and
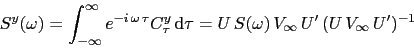 |
(82) |


Next: Short observation times
Up: OU-processes
Previous: Maximum likelihood estimation
Markus Mayer
2009-06-22