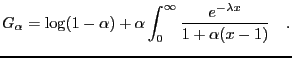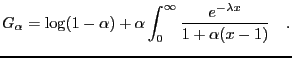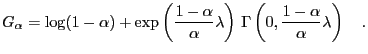

Next: Bibliography
Up: Analytical solutions for
Previous: Binomial distribution
A random variable 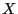 is distributed according to the exponential distribution if the cdf is
is distributed according to the exponential distribution if the cdf is
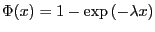 . We are interested in the shifted exponential distribution of
. We are interested in the shifted exponential distribution of
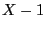 .
Using eq. (16) it is
.
Using eq. (16) it is
The integral is directly related to the incomplete gamma function
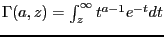 and a linear change of variables gives the result
and a linear change of variables gives the result
Note that
![$ \Gamma[0,z]$](img96.png) is related to the exponential integral function
is related to the exponential integral function
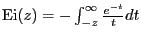 . i.e.
. i.e.
![$ \Gamma[0,z] = -\mathrm{Ei}(-z)$](img98.png) .
Figure 2.2 shows the graphs of
.
Figure 2.2 shows the graphs of 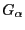 for different values of
for different values of
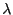 . Since
. Since
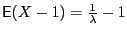 it is
it is
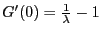 and
therefore
and
therefore 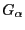 attains its maximum at
attains its maximum at 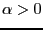 only for
only for 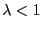 , i.e. those
shifted exponential distributions for which the mean is positive.
, i.e. those
shifted exponential distributions for which the mean is positive.
Fig. 1:
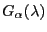 for the exponential distribution for different parameters
for the exponential distribution for different parameters 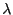 .
.
|
|
Unfortunately no closed form solution for
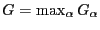 is available and one
has to resort to numerical techniques.
is available and one
has to resort to numerical techniques.
Fig.:
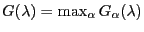 for the exponential distribution.
for the exponential distribution.
|
|


Next: Bibliography
Up: Analytical solutions for
Previous: Binomial distribution
Markus Mayer
2010-06-04