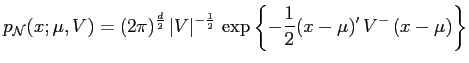

Next: Max-likelihood inference and EM-Algorithm
Up: The general setup for
Previous: The general setup for
The state variables are
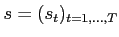 , the observed variables are
, the observed variables are
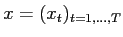 . The observation
probabilities are
. The observation
probabilities are
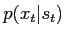 and the transition probabilities of the unobserved (''hidden'') states are
and the transition probabilities of the unobserved (''hidden'') states are
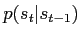 . Figure 1.1 shows the conditional dependency structure. The following abbrevations are
used very frequently:
. Figure 1.1 shows the conditional dependency structure. The following abbrevations are
used very frequently:
Fig.:
Basic conditional dependencies of Hidden Markov Models.
|
|
The 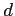 -dimensional normal distribution is denoted as
-dimensional normal distribution is denoted as
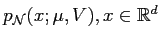 ,
,
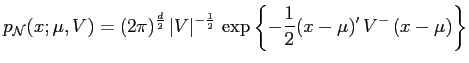 |
(1) |
Markus Mayer
2009-06-22
![]() -dimensional normal distribution is denoted as
-dimensional normal distribution is denoted as
![]() ,
,