

Next:
Up: Special results for EFM(2)
Previous:
For the particular form of 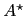 under specification EFM(2) the short-end slope becomes
under specification EFM(2) the short-end slope becomes
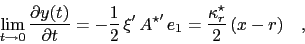 |
(65) |
i.e. a risk-free rate 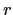 below the medium-term mean ('target')
below the medium-term mean ('target') 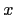 means a upward
sloping money-market curve. This makes economic sense since, in the medium term, in that case
the short rate is expected to rise. In EFM(2) the slope of the money-market curve is proportional to
the divergence between the short rate and the mid-term target.
means a upward
sloping money-market curve. This makes economic sense since, in the medium term, in that case
the short rate is expected to rise. In EFM(2) the slope of the money-market curve is proportional to
the divergence between the short rate and the mid-term target.
Markus Mayer
2009-06-22