

Next: Partial yield curve inversion
Up: The general -factor Gaussian
Previous: Finite time portfolio evolution
Bond prices depend on the covariance matrix 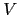 only through the affine term
only through the affine term 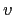 , and therefore
, and therefore
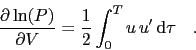 |
(33) |
Given 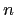 key-rates the model-covariance matrix
key-rates the model-covariance matrix 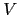 can be mapped to the key-rate
covariance matrix via
can be mapped to the key-rate
covariance matrix via
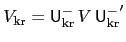 . This gives
. This gives
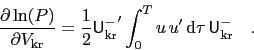 |
(34) |
With factor volatilities
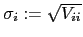 and diagonal volatility matrix
and diagonal volatility matrix
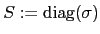 the correlation matrix reads
the correlation matrix reads 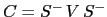 . This gives yield-sensitivities to volatility and correlation
. This gives yield-sensitivities to volatility and correlation
The sign of the yield-sensitivities depends crucially on the factor-correlations.
Markus Mayer
2009-06-22
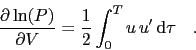
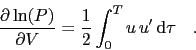
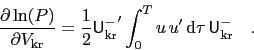
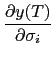
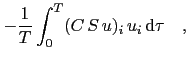
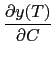
![$\displaystyle -{1\over 2}\,S^-\left[{1\over T}\int_0^T u\,u^\prime\,\mathrm{d}\tau\right]\,S^-\quad .$](img128.png)